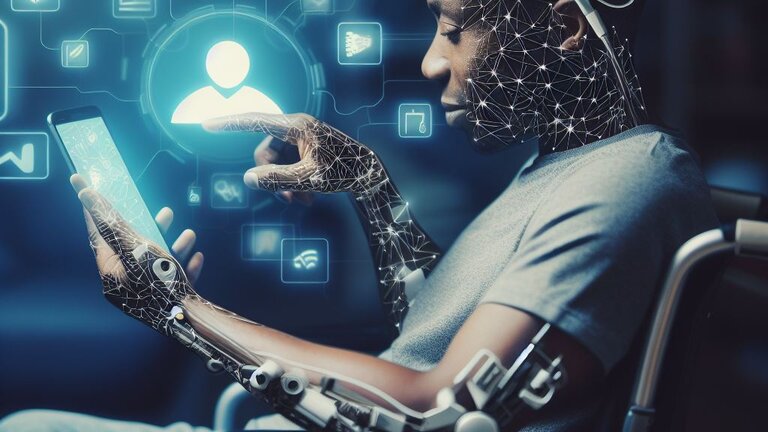
In the fast-paced world of innovation, not all revolutions make headlines. But there’s a quiet transformation happening — one that’s changing lives in profound ways. The rise of assistive technology is not just a story of tools and devices, but a movement of inclusion, independence, and dignity for people with disabilities.
From screen readers to smart wheelchairs, assistive tech is bridging the gap between limitation and opportunity. It’s redefining what it means to live, work, learn, and communicate in a world designed for the able-bodied — and it’s doing so with quiet power.
What Is Assistive Technology?
Assistive technology refers to any device or system that helps people with disabilities perform functions that might otherwise be difficult or impossible. These tools can range from simple (like hearing aids or magnifiers) to advanced (like eye-tracking communication software or bionic limbs).
It’s not about fixing disability — it’s about supporting ability.
Empowering Independence
For many in the disabled community, assistive tech represents more than convenience — it’s a pathway to freedom.
- Wheelchairs with terrain-sensing AI allow users to navigate difficult environments safely.
- Voice-controlled smart home devices give users full control over lighting, appliances, and security.
- Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices help non-verbal individuals express thoughts, emotions, and needs with clarity.
Each innovation puts more control back in the hands of the user, removing dependence on others and opening doors to greater autonomy.
Breaking Barriers in Education and Employment
Access to education and employment has long been a challenge for individuals with disabilities. Assistive tech is rapidly changing that:
- Speech-to-text tools help students with dyslexia or mobility issues participate in class.
- Braille displays and screen readers make digital content accessible for blind users.
- Real-time captioning and AI-powered transcription are transforming the experience for the deaf and hard of hearing in lectures, meetings, and interviews.
More importantly, these tools signal to society that inclusion is not charity — it’s a right.
The Role of Inclusive Design
The impact of assistive tech isn’t just in the tools, but in the shift toward inclusive design thinking. Tech companies, educators, and architects are increasingly building systems that accommodate a diverse range of users from the start.
This benefits everyone. Ramps, for instance, don’t only serve wheelchair users — they help parents with strollers, delivery workers, and elderly individuals. Voice assistants designed for accessibility also add convenience for busy households.
When you design for accessibility, you improve life for all.
Challenges Still Remain
Despite progress, the assistive tech revolution isn’t without barriers:
- High costs can make advanced devices inaccessible for many.
- Lack of awareness means people often don’t know what tools exist or how to access them.
- Inconsistent support systems across countries and regions can leave users without maintenance, training, or updates.
The next step in this revolution must be about scaling access and education, ensuring these life-changing tools reach those who need them most.
A Future Where Inclusion Is the Default
As AI, robotics, and wearable tech continue to evolve, the possibilities are immense:
- Smart glasses that convert text to speech in real time.
- Neural interfaces that allow users to control computers with their thoughts.
- Exoskeletons that assist with walking and lifting.
These aren’t distant dreams — they are emerging realities. And they represent a future where disability doesn’t limit participation in society.
Final Thought
The assistive tech movement may not make daily headlines, but its impact is felt deeply by millions around the world. It is a silent revolution, empowering individuals to live more fully, communicate more freely, and participate more equally.
Because real progress isn’t measured by how fast we build — but by how many people we bring along.